Time for Transformation Restoration and Renovation Ideas

Exploring Restoration and Renovation Ideas
Preserving History
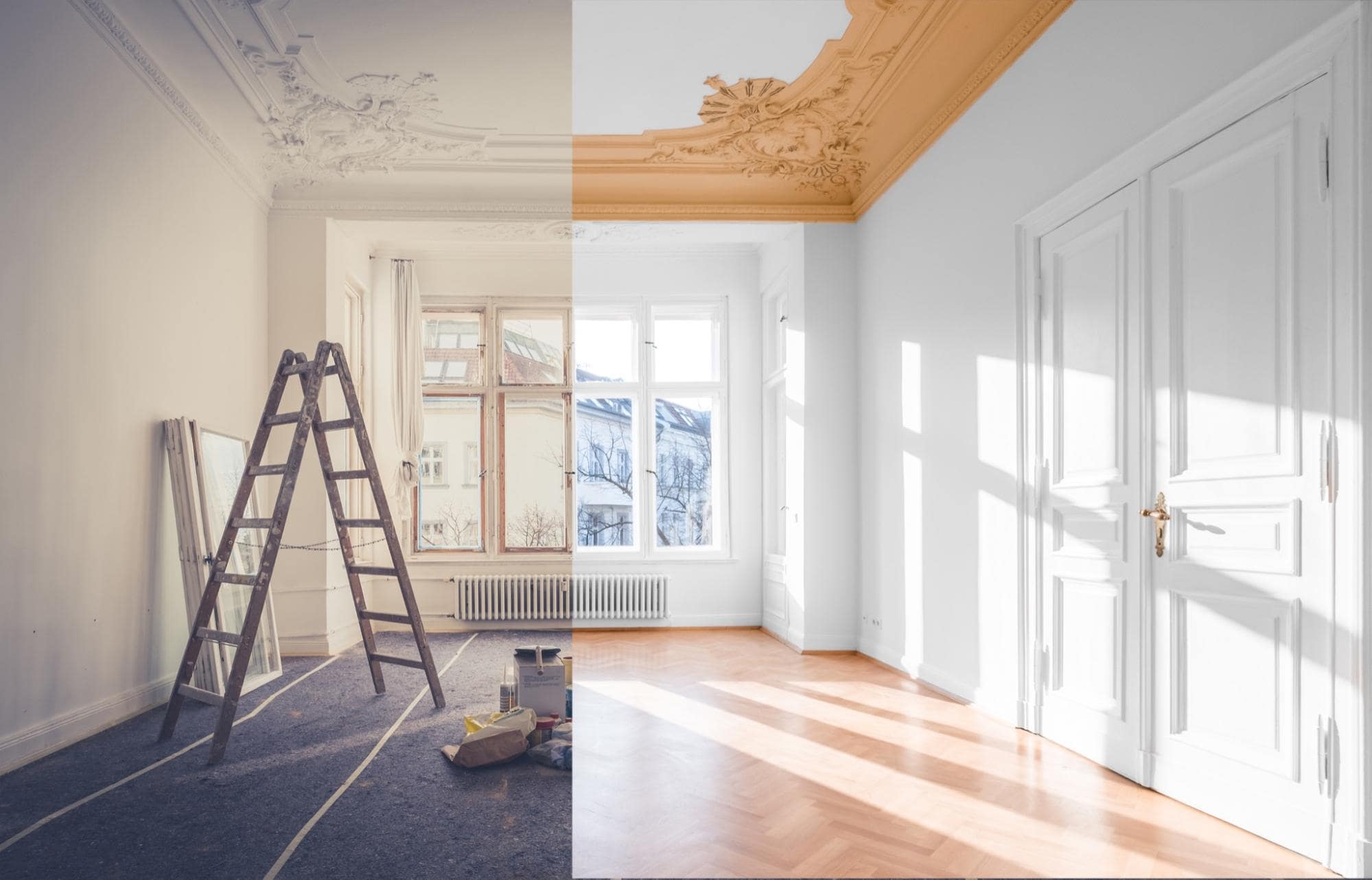
Restoration and renovation projects offer a unique opportunity to preserve the history and character of a property while modernizing it for contemporary living. Whether it’s a historic home, a heritage building, or a beloved family heirloom, restoring and renovating these spaces requires careful planning and attention to detail. By preserving original features and architectural elements, such as crown molding, hardwood floors, and decorative trim, you can honor the past while creating a space that meets the needs of today’s homeowners.
Modernizing Spaces
In addition to preserving history, restoration and renovation projects also provide an opportunity to modernize and update spaces for improved functionality and comfort. This may involve opening up floor plans to create more spacious and airy interiors, installing energy-efficient windows and doors, or updating kitchens and bathrooms with modern appliances and fixtures. By blending historic charm with contemporary amenities, you can create a space that seamlessly combines the best of both worlds.
Embracing Sustainable Design
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for homeowners, and restoration and renovation projects offer an opportunity to incorporate eco-friendly design principles. This may include using reclaimed materials, such as salvaged wood or vintage fixtures, to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact. Additionally, integrating energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels or geothermal heating, can help reduce utility costs and make your home more environmentally friendly.
Enhancing Curb Appeal
The exterior of a property plays a crucial role in its overall appeal, and restoration and renovation projects often involve enhancing curb appeal to create a lasting first impression. This may include repainting the exterior, updating landscaping, or restoring architectural details such as porches, columns, or trim. By investing in curb appeal, you can increase the value of your property and make it more attractive to potential buyers or tenants.
Creating Functional Outdoor Spaces
In addition to improving the interior of a property, restoration and renovation projects also often involve creating functional outdoor spaces for relaxation and entertainment. This may include adding a deck or patio for outdoor dining and entertaining, installing a fire pit or outdoor kitchen for cozy evenings spent al fresco, or landscaping the yard to create a tranquil garden oasis. By extending your living space outdoors, you can maximize the enjoyment of your property and increase its value.
Investing in Quality Materials
When undertaking restoration and renovation projects, it’s essential to invest in quality materials that will stand the test of time. This may involve using durable hardwoods for flooring, high-quality finishes for cabinetry and countertops, or premium fixtures and appliances for kitchens and bathrooms. While quality materials may come with a higher upfront cost, they can ultimately save you money in the long run by reducing maintenance and replacement expenses.
Prioritizing Safety and Compliance
Ensuring the safety and compliance of a property is paramount during restoration and renovation projects. This may involve updating electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems to meet current building codes, installing smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, or addressing any structural issues