Achieving Operational Excellence Strategies for Success
Achieving Operational Excellence: Strategies for Success
Operational excellence is more than a lofty goal; it’s a commitment to continuously improve and streamline every aspect of business operations. In this exploration, we delve into the key strategies that propel organizations towards operational excellence.
Strategic Vision and Leadership
Operational excellence begins with a clear strategic vision and strong leadership. Leaders set the tone for a culture of continuous improvement and guide the organization towards its operational goals. A shared vision ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned, working towards common objectives.
Process Optimization and Efficiency
At the heart of operational excellence lies process optimization. Analyzing and refining processes to eliminate inefficiencies and redundancies is essential. This involves a meticulous examination of workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing changes that enhance efficiency. Continuous improvement methodologies like Six Sigma contribute significantly to this aspect.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
In the era of big data, operational excellence is closely tied to data-driven decision-making. Organizations that leverage data analytics gain valuable insights into their operations. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making, as trends, patterns, and key performance indicators become the foundation for strategic choices.
Employee Empowerment and Engagement
Employees are the driving force behind operational excellence. Empowering and engaging them fosters a culture of ownership and accountability. Providing training, recognizing achievements, and involving employees in decision-making processes contribute to a motivated workforce dedicated to achieving operational excellence.
To explore deeper insights into achieving operational excellence, organizations can visit Operational excellence. This link serves as a gateway to a wealth of resources, offering guidance on best practices and emerging trends in operational excellence.
Innovative Technology Adoption
Embracing innovative technologies is a crucial element in the pursuit of operational excellence. From automation and artificial intelligence to advanced software solutions, technology streamlines operations and enhances efficiency. Integration of these tools provides organizations with the agility to adapt to changing market dynamics.
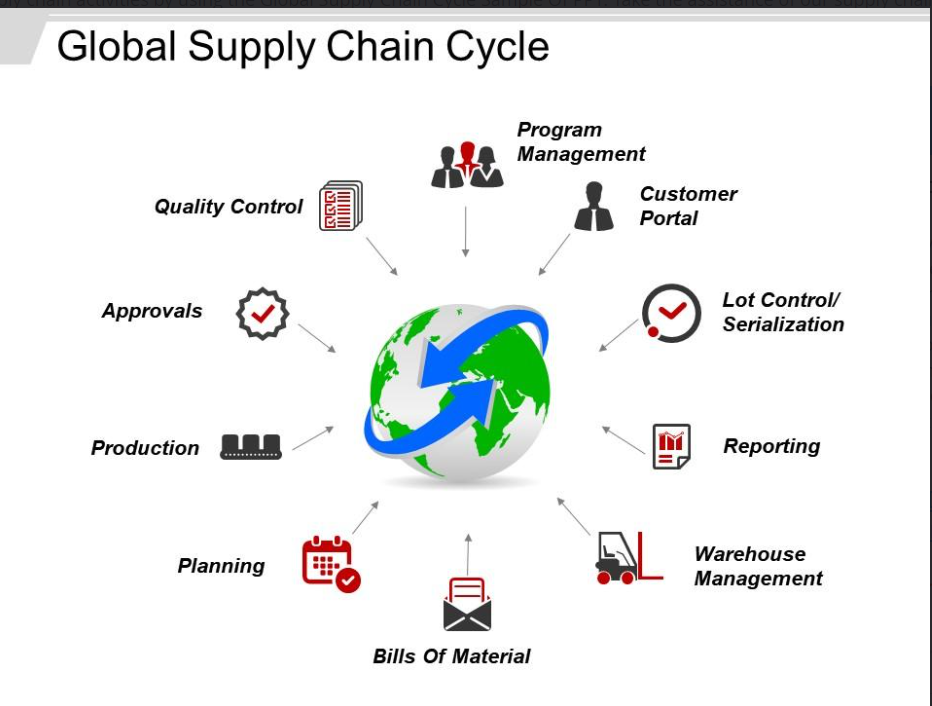
Supply Chain Optimization
Operational excellence extends beyond the organization to the entire supply chain. Organizations must optimize their supply chain to ensure seamless operations. This involves building strong relationships with suppliers, implementing efficient logistics, and adopting strategies like just-in-time manufacturing to minimize waste and costs.
Risk Management Strategies
In the pursuit of operational excellence, organizations must also be adept at managing risks. This includes identifying potential risks, creating contingency plans, and implementing strategies to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events. A proactive approach to risk management ensures operational continuity and resilience.
Customer-Centric Focus
Operational excellence is not just about internal processes; it’s also about delivering value to customers. A customer-centric approach involves understanding customer needs, providing exceptional service, and continuously seeking ways to enhance the customer experience. Satisfied customers become advocates for the brand.
In the grand scheme of business success, operational excellence emerges as a guiding principle, a north star that organizations strive to reach. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, embracing technology, and putting customers and employees at the center of operations, organizations pave the way for sustained excellence. The journey towards operational excellence is